Astronomical Information | 2016 | March
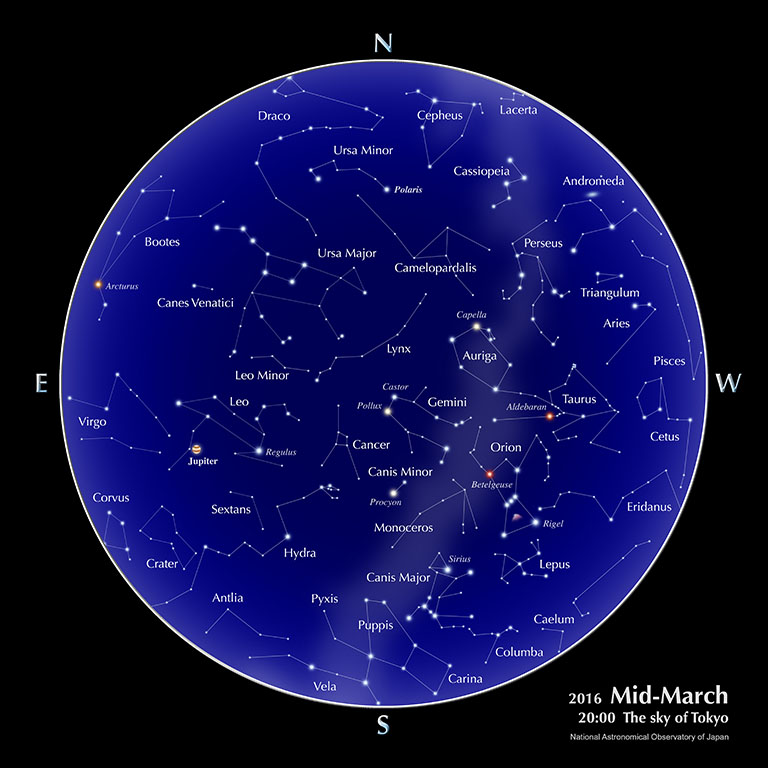
The sky of Tokyo
Calendar (February)
| 2 | Last Quarter Moon |
| 8 | Jupiter at opposition |
| 9 | Total solar eclipse (A partial solar eclipse can be seen from all of Japan) Reference: Local Prediction of the Solar Eclipse / New Moon |
| 16 | First Quarter Moon |
| 20 | Vernal Equinox Day [Shunbun-no-hi] (national holiday) / Vernal equinox (Sun’s ecliptic longitude 0°) |
| 21 | Holiday |
| 23 | Full Moon |
| 24 | Mercury at superior conjunction |
| 25 | Saturn at stationary point |
The days for the peak activities of the meteor showers are based on the predictions of IMO (International Meteor Organization).
Planets
- Mercury
- Mercury is positioned close to the Sun and not suited for observations. It reaches superior conjunction on the 24th.
- Venus
- Venus is positioned low in the eastern sky before sunrise, but its apparent location is close to the Sun so it is not suited for observations.
- Mars
- Mars moves from the constellation Libra to the constellation Scorpius. It can be seen in the southern sky before sunrise. Its brightness is 0.3 magnitude to -0.5 magnitude.
- Jupiter
- Jupiter, located in the constellation Leo, can be seen in the southern sky around 19:00, when viewed from Tokyo. It reaches opposition on the 8th, presenting us with an opportunity to observe it. Its brightness is -2.5 magnitude to -2.4 magnitude.
- Saturn
- Saturn, located in the constellation Ophiuchus, can be seen in the southern sky before sunrise. Its brightness is 0.5 magnitude to 0.4 magnitude.
Source: Ephemeris Computation Office, NAOJ
With the “Sky Viewer” you can easily explore the appearance of a typical urban night sky (planets and constellations are visible).The Celestial Phenomena section of the glossary explains the planetary phenomena terms: greatest elongation, opposition, conjunction, stationary, etc.