This Year’s Largest Full Moon (December, 2017)

Let’s enjoy the various types of Moon!
The full moon of December 4 is the closest of all the full moons (Note 1) this year. The Moon becomes full phase at 0:47, just after the date has changed on December 4, and passes through the perigee (Note 2) at 17:46. At the time of the full moon, the geocentric distance (Note 3) is about 358,000 kilometers, and the Moon’s apparent diameter (Note 4) is 33 arcminutes 22 arcseconds. In the next month, when the Moon reaches full phase on January 2, 2018, it approaches even closer to the Earth than on December 4. The geocentric distance is 357,000 kilometers and the apparent diameter is arc33 minutes 30 arcseconds at the time of the full moon.
When the Moon is close to the Earth, the Moon looks big. The figure above is a conceptual diagram comparing the apparent diameter of the Moon during the full moon on December 4, which is the closest Moon, and the full moon on June 9, which is the furthest of this year. If you could place the closest full moon and the furthest full moon side-by-side as shown in the figure above, you could easily see the size difference. But, you cannot line up the real moons in the night sky to compare the sizes because you can only see one Moon in the real sky. Since it is not easy to measure the size without comparing them, it will be very difficult to notice the change in the size of the Moon just by looking at it.
Changes in the Moon's Distance
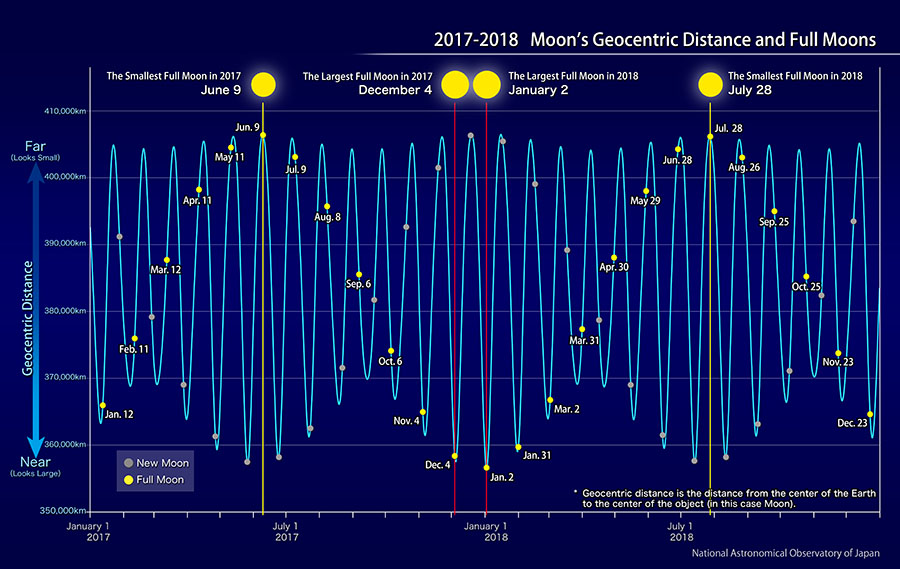
The Moon orbits around the Earth. The Moon’s orbit is elliptical, so the distance between the Earth and the Moon is not always the same. The orbit of the Moon changes as it is affected by the gravity of the Sun and the Earth. So, as shown in the figure above, the geocentric distances when the Moon is at the perigee and the apogee are different each time. The geocentric distance during the full moon varies from approximately 356,000 kilometers to 406,000 kilometers. The apparent diameter of the Moon is large when the Earth and Moon are close; and small when they are far from each other. The apparent diameter of the closest full moon is 14 percent larger than that of the furthest full moon. Also, the largest full moon appears 30 percent brighter than the smallest full moon.
Recently, when the Moon approaches the Earth, it is called a "super moon" and it is talked about on the news. However, the Moon looks different every time. The Moon changes its phases and shape: the waxing crescent, the half moon, the full moon, etc. Sometimes it approaches a bright star. How about gazing at the night sky sometimes and enjoying the various attractive moons?
(Note 1) “Full moon” in astronomy refers to the Moon at the moment when it is in the opposite direction from the Sun, as seen from the center of the Earth. Back
(Note 2)“Perigee” is the point where the Moon is the closest to the Earth. “Apogee” is the point where it is the furthest. Back
(Note 3) “Geocentric distance” is the distance between the center of the Earth and the center of the Moon. Back
(Note 4)“Apparent diameter” is the apparent size of the celestial object. The apparent diameters shown on this page are calculated based on the geocentric distance. Back
About the Supermoon
"Supermoon" is not an astronomical term and its definition is not clear.