About TMT
The Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) is an optical-infrared, next-generation extremely large astronomy telescope with a 30-m aperture that is currently under construction. Construction of TMT is progressing through international cooperation between the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (in Japan), the University of California and California Institute of Technology (in the United States), the National Research Council (in Canada) and the Department of Science and Technology (in India). In the United States, preparations are underway for the National Science Foundation (NSF) to officially join through federal funding, and currently, the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA) is participating as an associate member. Japan will be responsible for vital components, including the construction of the telescope structure, the light-gathering primary mirror, and science instruments. Once completed, the telescope will achieve an unprecedented level of resolution and sensitivity.
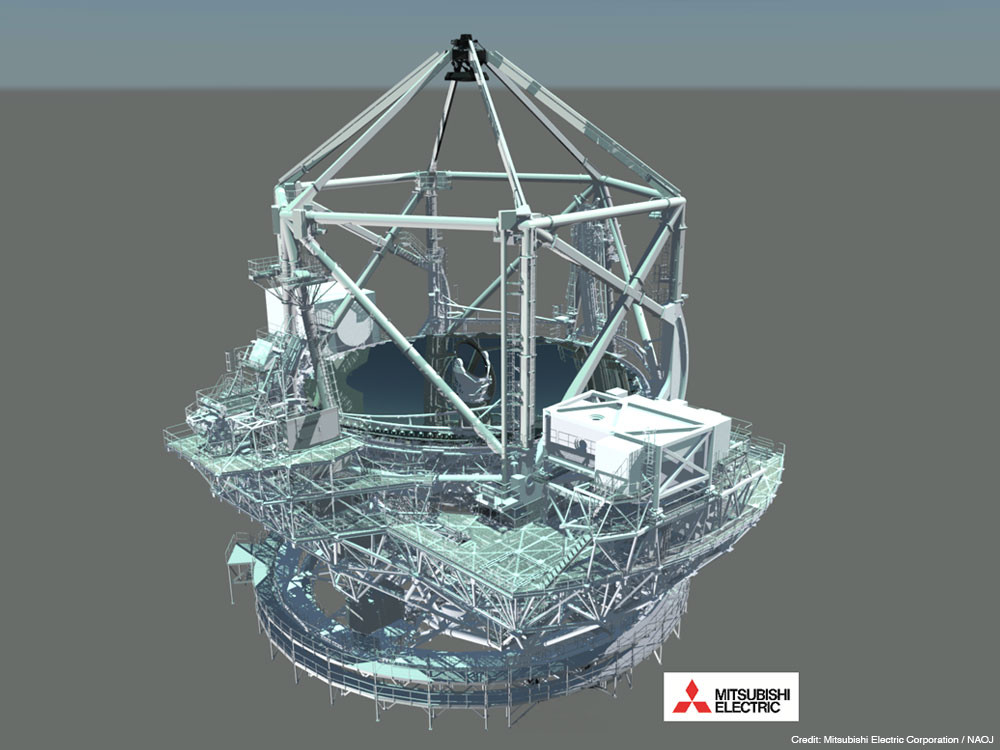
The defining feature of TMT is its extremely large primary mirror. As its name implies, the primary mirror is 30 meters in diameter. The primary mirror is composed of 492 smaller segments of hexagonal mirrors. In order to make the best use of the light-collecting power of the primary mirror, TMT will be equipped with state-of-the-art technology, including an adaptive optics system that compensates for atmospheric fluctuations in real time. Development is also underway for first light instruments to be put into operation upon completion of the telescope, including IRIS (InfraRed Imaging Spectrograph), WFOS (Wide Field Optical Spectrometer), and MODHIS (Multi-Objective Diffraction-limited High-Resolution Infrared Spectrograph).
Research
A new world of optical-infrared astronomy will be opened when TMT is completed. TMT is expected to revolutionize many research themes that have been started by the Subaru Telescope and other telescopes; for example the search for the farthest galaxies and the first stars in the early Universe; efficient spectroscopic observation of many galaxies and stars; and direct imaging and spectroscopic observation of extrasolar planets.
Specifications
| Aperture of primary mirror | 30 meters (492 segments) |
|---|---|
| Optics | Ritchey-Chrétien |
| Focus | Nasmyth focus |
| Combined focal length | 450 meters |
| Field of view | 15 arcminutes |
| Primary mirror F-number | 1 |
| Diffraction limit | 8 arc milliseconds (1 micrometer in wavelength) |
| Observing wavelength | 0.31 to 28 micrometers |
| First light instruments | IRIS (InfraRed Imaging Spectrograph) WFOS (Wide Field Optical Spectrometer) MODHIS (Multi-Objective Diffraction-limited High-Resolution Infrared Spectrograph) |
History
| April 2005 | ELT (Extremely Large Telescope) Project Office established |
|---|---|
| July 2009 | Maunakea, Hawai‘i Island chosen as site for TMT |
| April 2010 | ELT Project Office renamed as the TMT Project Office |
| 2012 | TMT Project Office renamed as the TMT-Japan Project Office |
| 2013 | First segmented mirror blank complete |
| May 2014 | Thirty Meter Telescope International Observatory (TIO) established |
| August 2014 | TMT listed on the MEXT Roadmap 2014 |
| 2015 | Begin mass production of aspherical grinding |
| December 2016 | Final Design Review of the telescope structure complete |
| September 2017 | Preliminary Design Review of IRIS complete |
| August 2019 | TMT-Japan Project Office renamed as the TMT Project |
| December 2023 | TMT listed on the MEXT Roadmap 2023 |
